Table of Contents
Pubic lice are minute insects that lives and leaves eggs in the pubic region. They can also spread in eyebrows and armpit hairs.
Causes of Pubic Lice
They can be spread through sexual intercourse, and common among teenagers. In rare cases, they can be spread through direct contact with things used by an infected person, such as toilet seats, blankets, sheets, or even bathing suits (women may try on at bikini stores).
Animals such as dogs, can’t spread pubic louse to humans.
Those who have many sexual partners are at high risk of pubic lice. Or even those who share bedding and clothes with an infected person.
Pubic Lice Symptoms
As with other types of lice infection, pubic lice cause itching in pubic hair area. Itching is usually worse during bedtime, and usually starts as soon as one gets infected with. In some cases, itching starts to show up a couple of weeks or even a month after contact.
Skin in pubic region will also turn grayish-blue in color when infected, as well as sores caused by bites and of course, scratching.
Diagnosis for Pubic Lice
Though bites and scratches can be detected easily, healthcare providers usually conduct a series of tests to provide a more thorough diagnosis. Usually, doctors will check for small grayish-white oval-shaped eggs (called nits) that are usually attached to the shaft of pubic hairs. They can also find adult lice.
Scratches are tell-tale signs for infection.
In young children, pubic eyes can cause eye infection, which is why their eyelashes should be checked using a magnifying glass.
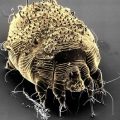
Adult louse are actually easily identified through a microscope, and health professionals call them “true crabs” for their crab-like appearance under a microscope.
Teenagers must be checked for STI (sexually transmitted infection) when infected with pubic lice.
Pubic Lice Treatment
Pubic louse is usually treated using a medication called permethrin, a synthetic insecticide used against disease-carrying insects. This topical medication must be applied thoroughly to the pubic region and its surrounding area, and left for 10 minutes, or as directed by the doctor.
The pubic region must be rinsed and combed using a special comb (fine-toothed comb) to get rid of the eggs.
Doctors may also advise the application of vinegar to the pubic region when combing to thoroughly get rid of eggs.
In most cases, one treatment is usually enough. Should second treatment be needed, it must be applied at least four days to a week after the first treatment.
Other OTC medications used for treatment of lice include Rid and Nix and Malathione lotion.
Care Tips
When treating pubic lice, it is also vital to wash beddings and clothing with hot water.
Items that can’t be washed must be sprayed using a medicinal spray (can be bought from stores) to kill the lice. Those that can’t be sprayed must be placed inside a sealed plastic bag for at least 10 days to suffocate and kill the lice.
Of course, those with whom an infected person have shared bed or have had sexual intercourse with must be treated concurrently.
Those who have this infection must also get checked for STIs (sexually transmitted infection).





 I love to write medical education books. My books are written for everyone in an easy to read and understandable style.
I love to write medical education books. My books are written for everyone in an easy to read and understandable style.