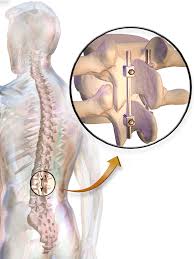
About Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease
Lumbar degenerative disc disease is the term used to refer to the sensation of pain in the lower back due to loss of water in the spinal discs. The loss of water content can be attributed to many factors including wear and tear or natural aging process. This causes the discs to come in contact with each other with every movement. It is unable to absorb shock as efficiently as it is supposed to.
The level of pain varies depending on the extent of the degenerative disc disorder. Some pain might be minor while others develop into chronic pain.
Causes
Even though there is no clear cut reason for lumbar degenerative disc disease, these causes can be attributed to one of two (or a combination of causes). The first one is due to an inflammation in the spinal discs. When the discs come into contact with each other with every movement, the surrounding nerves in the spine are irritated. This inflammation is what is causing the painful sensation when you attempt any movement involving the lower back.
An abnormality in the disc’s micro motion is another potential cause for lumbar degenerative disc disease. This often takes place when the spinal discs’ outer rings become worn down and unable to absorb stress effectively.
Symptoms
The most common symptom of lumbar degenerative disc disorder is a tolerable but continuous pain. Occasionally, the intensity of the pain will flare up, but it can vary to a great degree. Although symptoms can be varied from one person to another, some common symptoms include the following:
- Pain centered in the lower back area, which may extend to the hips and legs;
- Chronic lower back pain that lasts for more than 6 weeks at a time;
- Pain that worsens with extended period of sitting or when doing activity that require lifting of heavy weight;
- Pain that worsens with any sudden movement such as bending or stretching.
Risk Factors
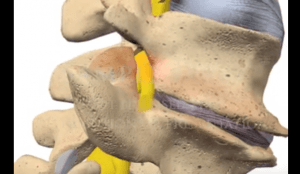
Any activity that puts a lot of stress on your spine and lower back can also be a risk factor for lumbar degenerative disc disease. In some cases, injuries can result to a disc problem as well.
Diagnosis
If you think you are suffering from lumbar degenerative disease, your doctor will conduct a thorough examination. Special attention will be given to the lower back and your lower extremities when conducting the physical examination. You will also undergo X-ray and MRI to determine the condition of your spinal discs.

 I love to write medical education books. My books are written for everyone in an easy to read and understandable style.
I love to write medical education books. My books are written for everyone in an easy to read and understandable style.